Leadership
Wood And Fire Risk: Where Fallacy And Facts Meet Homebuilding
Here, from Construction Physics' Brian Potter, is an evidence-based look at one of new-home construction's more combustible debates.
It's one of residential construction's combustible topics.
Brian Potter is a structural engineer who writes here on "Wood Construction and the Risk of Fire."
History, physics, data science, engineering and materials science, regulation and local/regional/state and federal policy, construction practices, climate, environmental science and geography, insurance claims, special interest narratives, all get the 3rd degree in Potter's deep dive – sporting both literature search and first-hand reporting and research chops – into one of the 2020s hottest challenges for housing leaders.
Potter starts with a caveat in his analysis, stating that his analysis here covers light framed wood construction, not heavy timber construction, such as CLT. This speaks to the vast majority of timber-frame residential building in the U.S.
Risk he focuses on is not reputational, rhetorical, or narrative, but rather risk to health and safety, and risk to property damage.
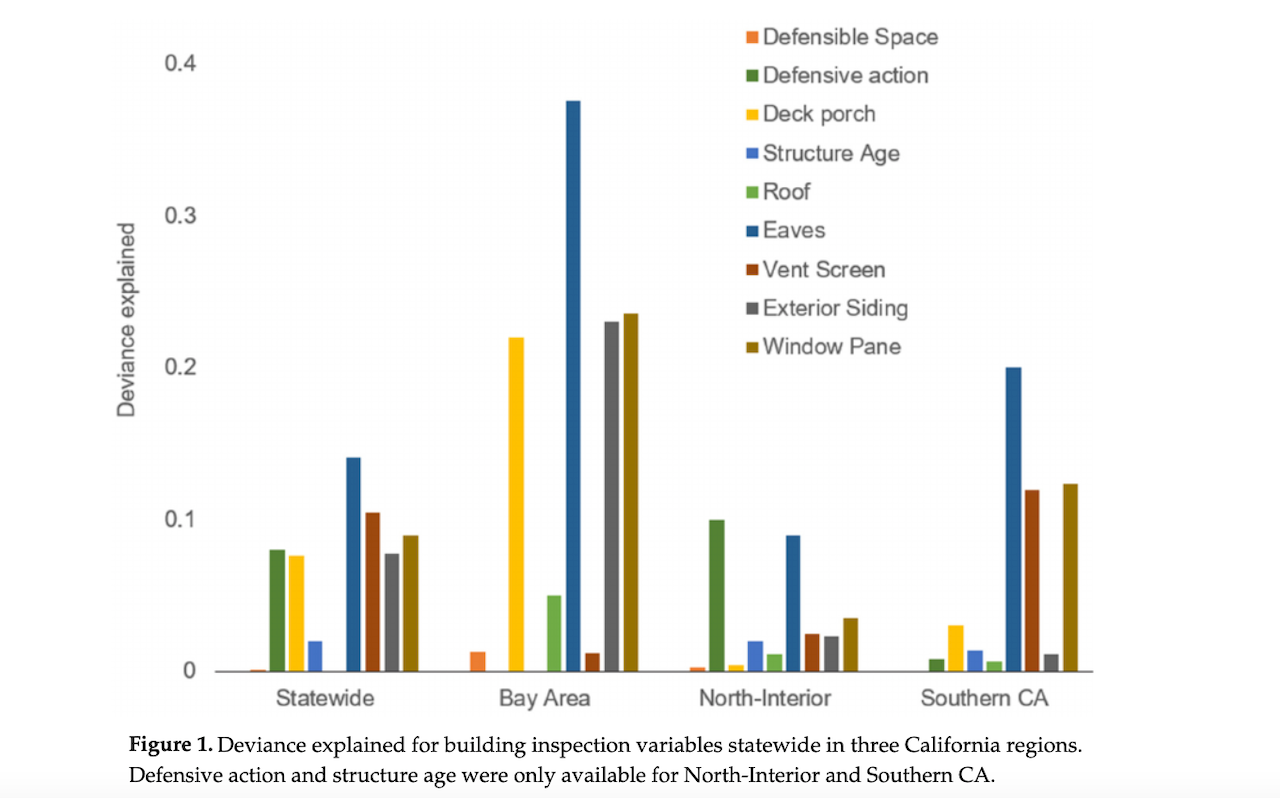
In 21 graphics, tables, physics equations, heat-maps, and diagrams, Potter works through the issues with wood and fire, alternative construction material options, trends, tactics, and scenarios.
He concludes:
Overall, it seems like wood construction does somewhat increase the potential risk of fire, mostly by allowing fires that do occur to be somewhat deadlier and more destructive. However, this effect is mostly swamped by other factors such as what state and city you live in, or whether you live in a house or an apartment. For a wood apartment in Salt Lake City, the risk of fire is vanishingly small; for a wood single family home in a tiny town in Arkansas, it’s much larger.
The most important factor for fire risk in a home is whether or not it’s sprinklered. Fire sprinklers reduce the risk of fire by an enormous amount, and sprinklered wood construction seems to perform about as well as sprinklered non-combustible construction. And sprinklers are cheap, costing about $1-2 per square foot (much less than it would cost to say, change a wood house to concrete).
For wildfires specifically, we see something similar - construction details such as fire protected eaves and class A roofs, along with things like community density, matter far more than whether your home is wood or steel.


